Math
The Math Routines manipulate BCD and decimal numbers and store/transfer data.
Note: Most of the Math routines are undocumented in the Nutting Manual. Their definitions and usage are largely found in the system ROM source listing and Bally On-Board ROM Subroutines.
Math System Routines
Undocumented routines are marked with an asterisk (*)
Need documentation for most math routines
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BCDADD* | BCD add |
| BCDCHS* | BCD change sign |
| BCDDIV* | BCD divide |
| BCDMUL* | BCD multiply |
| BCDNEG* | BCD negate |
| BCDSUB* | BCD subtract |
| DABS* | Decimal absolute value |
| DADD* | Decimal add |
| DSMG* | Decimal convert to sign magnitude |
| INDEXB | Returns byte at address + displacement |
| INDEXN | Look up a given nibble in a linear list |
| INDEXW | Look up a given word in a linear list |
| MOVE | Block transfer, copies bytes from source to destination |
| NEGT* | Decimal negate |
| RANGED | Generate ranged random number |
| SETB | Store byte at a specified address |
| SETW | Store 16-bit word at specified address |
| SHIFTU* | Shift up digit in A |
| STOREN | Store 4-bit nibble in a linear list |
Math System Routine Descriptions
BCDADD
BCD ADDITION
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM BCDADD or SYSSUK BCDADD DW (arg 1) DB (size/2 + 1) DW (arg 2) |
| Arguments: | B = SIZE/2 + 1 DE = Argument 1 HL = Argument 2 |
| Output: | DE = Answer |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
BCDCHS
BCD CHANGE SIGN
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM BCDCHS or SYSSUK BCDCHS DB () DW () |
| Arguments: | B = HL = |
| Output: | |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
BCDDIV
BCD DIVISION
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM BCDDIV or SYSSUK BCDDIV DW (arg 1) DB () DW (arg 2) |
| Arguments: | B = DE = HL = Argument 2 |
| Output: | ??? |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
BCDMUL
BCD MULTIPLY
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM BCDMUL or SYSSUK BCDMUL DW (arg 1) DB () DW (arg 2) |
| Arguments: | B = DE = HL = |
| Output: | DE = Answer |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
BCDNEG
BCD NEGATE TO DECIMAL
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM BCDNEG or SYSSUK BCDNEG DW () DB () |
| Arguments: | B = DE = |
| Output: | ??? |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
BCDSUB
BCD SUBTRACTION
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM BCDSUB or SYSSUK BCDSUB DW (arg 1) DB () DW (arg 2) |
| Arguments: | B = DE = HL = |
| Output: | DE = Answer |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
DABS
DECIMAL ABSOLUTE VALUE
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM DABS or SYSSUK DABS DW () DB () |
| Arguments: | B = DE = |
| Output: | |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
DADD
DECIMAL ADDITION
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM DADD or SYSSUK DADD DW (arg 1) DB () DW (arg 2) |
| Arguments: | B = DE = HL = |
| Output: | ??? |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
DSMG
DECIMAL CONVERT TO SIGN MAGNITUDE
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM DSMG or SYSSUK DSMG DW (arg 1) DB (size/2 + 1) |
| Arguments: | B = DE = |
| Output: | ??? |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
INDEXB
INDEX BYTE
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM INDEXB or SYSSUK INDEX DW (base address) |
| Arguments: | A = Displacement (0–255) HL = Base address of table |
| Output: | A = Entry looked up HL = Address of entry looked up |
| Description: | INDEXB returns the byte at address (Base address) + (Displacement) |
INDEXN
INDEX NIBBLE
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM INDEXN or SYSSUK INDEXN DW (base address) |
| Arguments: | C = Nibble displacement (0–255) HL = Base address of table |
| Output: | A = Nibble value |
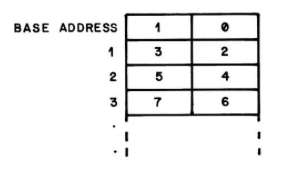
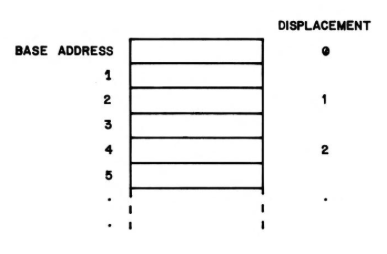
| Notes: | Indexing illustration below |
| Description: | INDEXN looks up a specified nibble in a linear list. |
INDEXW
INDEX WORD
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM INDEXW or SYSSUK INDEXW DW (base address) |
| Arguments: | A = Displacement (0–255) HL = Base address of table |
| Output: | DE = Entry looked up HL = Address of entry looked up |
| Notes: | Indexing illustration below |
| Description: | None |
MOVE
MOVE BYTES
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM MOVE or SYSSUK MOVE DW (destination) DW (number of bytes) DW (source) |
| Arguments: | DE = Destination address HL = Source address BC = Number of bytes to transfer |
| Description: | MOVE uses LDIR to copy bytes from source to destination. |
NEGT
DECIMAL NEGATE
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM NEGT or SYSSUK NEGT DB (B) DW (HL) |
| Arguments: | B = HL = |
| Output: | ??? |
| Notes: | None |
| Description: |
RANGED
RANGED RANDOM NUMBER
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM RANGED or SYSSUK RANGED DB (N) |
| Arguments: | A = Range |
| Output: | A = Random Number (0 to Range - 1) |
| Notes: | If N is a power of 2, it is considerably faster to use N=0, which causes an 8-bit value to be returned without ranging. Use an AND instruction to range it yourself. RANGED uses a polynomial shift register RANSHT in system RAM. RANGED is called in GETNUM while waiting for game selection/parameter entry. Thus each execution of a program will receive different random numbers. For “predictable” random numbers, alter RANSHT yourself after parameter acceptance. |
| Description: | Returns a ranged random number. |
SETB
STORE BYTE
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM SETB or SYSSUK SETB DB (value to store) DW (address) |
| Arguments: | A = Byte value to store HL = Storage address |
| Description: | Stores an 8-bit value at a specified address. |
SETW
STORE WORD
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM SETW or SYSSUK SETW DW (value to store) DW (address) |
| Arguments: | DE = Word value to store HL = Storage address |
| Description: | Stores a 16-bit value at a specified address. |
SHIFTU
SHIFT UP DIGIT IN A
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM ????
|
| Arguments: | |
| Notes: | |
| Description: | Shift up digit in A |
STOREN
STORE NIBBLE
| Calling Sequence: | SYSTEM STOREN or SYSSUK STOREN DW (base address) |
| Arguments: | C = Nibble displacement (not loaded) HL = Base address A = Nibble value to store (not loaded) |
| Description: | STOREN is the inverse of INDEXN but functions identically. |